Pancreatic cancer is the fourth leading cause of cancer related death in the US and exhibits aggressive features with short survival rate and high mortality. Therefore, it is important to understand the molecular mechanism(s) involved in the aggressive growth of pancreatic cancers, and further design novel targeted therapies for its treatment with better treatment outcome.
In a recent study, researchers from the Wayne State University School of Medicine found that the expression of miR-221 was significantly up-regulated in pancreatic cancer cell lines and tumor tissues compared to normal pancreatic duct epithelial cells and normal pancreas tissues. Moreover, they found that the pancreatic cancer patients with high miR-221 expression had a relatively shorter survival compared to those with lower expression, suggesting that miR-221 could be an oncogenic miRNA and a prognostic factor for poor survival of patients. Interestingly, transfection of miR-221 inhibitor suppressed the proliferative capacity of pancreatic cancer cells with concomitant up-regulation of PTEN, p27kip1, p57kip2, and PUMA, which are the tumor suppressors and the predicted targets of miR-221. Most importantly, they found that the treatment of pancreatic cancer cells with isoflavone mixture (G2535), formulated 3,3’-diindolylmethane (BR-DIM), or synthetic curcumin analogue (CDF) could down-regulate the expression of miR-221 and consequently up-regulate the expression of PTEN, p27kip1, p57kip2, and PUMA, leading to the inhibition of cell proliferation and migration of MiaPaCa-2 and Panc-1 cells. These results provide experimental evidence in support of the oncogenic role of miR-221 and also demonstrate the role of isoflavone, BR-DIM, and CDF as potential non-toxic agents that are capable of down-regulation of miR-221. Therefore, these agents combined with conventional chemotherapeutics could be useful in designing novel targeted therapeutic strategy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer for which there is no curative therapy.
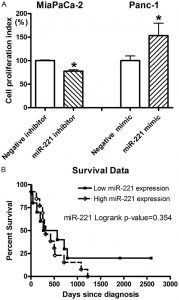
A: Transfection of miR-221 inhibitor into MiaPaCa-2 cells significantly inhibited cell proliferation while the transfection of miR-221 mimic into Panc-1 cell significantly promoted cell proliferation as tested by MTT assay (*: P< 0.05). B: Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that the pancreatic cancer patients with lower miR-221 expression had a relatively longer survival compared to the patients with higher expression of miR-221.
Related Service
miRNA Microarray Service – LC Sciences provides a microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling service using microarrays based on our in-house developed µParaflo® technology platform. We have standard arrays for all mature miRNAs of all species available in the latest version of the miRBase database (Release 21, July 2014). Our service is comprehensive and includes sample labeling, array hybridization, image data processing and in-depth data analysis. Two-three weeks after receiving your total RNA samples, we’ll send you both the raw and fully analyzed data. [Learn more…]
Reference
Sarkar s et al. (2013) Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27kip1, p57kip2, and PUMA. Am J Cancer Res 3(5), 465-477. [article]
