Exosomes originating from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSC-exos) have become a novel strategy for treating various diseases owing to their ability to regulate intercellular signal communication. However, the potential of hucMSC-exos to improve placental injury in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome and its underlying mechanism remain unclear. The objective of this study led by Shandong First Medical University was to explore the potential application of hucMSC-exos in the treatment of obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome and elucidate its underlying mechanism. In this study, hucMSC-exos ameliorated the functional impairment of trophoblasts caused by antiphospholipid antibodies in vitro and attenuated placental dysfunction in mice with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome by delivering miR-146a-5p. They used LC Sciences’ miRNA microarray service on Total RNA that was extracted from hucMSC-exos. Exosomal miR-146a-5p suppressed the expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and inhibited the activation of NF-κB signaling, leading to the down-regulation of IL-1β and IL-18 to rescue inflammation and modulation of Cleaved-CASP3, BAX, and BCL2 to inhibit apoptosis in HTR8/SVneo cells and mice placenta. This study identified the potential molecular basis of how hucMSC-exos improved antiphospholipid antibody-induced placental injury and highlighted the functional importance of the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis in the progression of obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. More importantly, this study provided a fresh outlook on the promising use of hucMSC-exos as a novel and effective treatment approach in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome.
MiRNA sequencing analysis of hucMSC-exos and comprehensive analysis of genes and pathways involved in hucMSC-exos treatment based on mRNA high-throughput sequencing
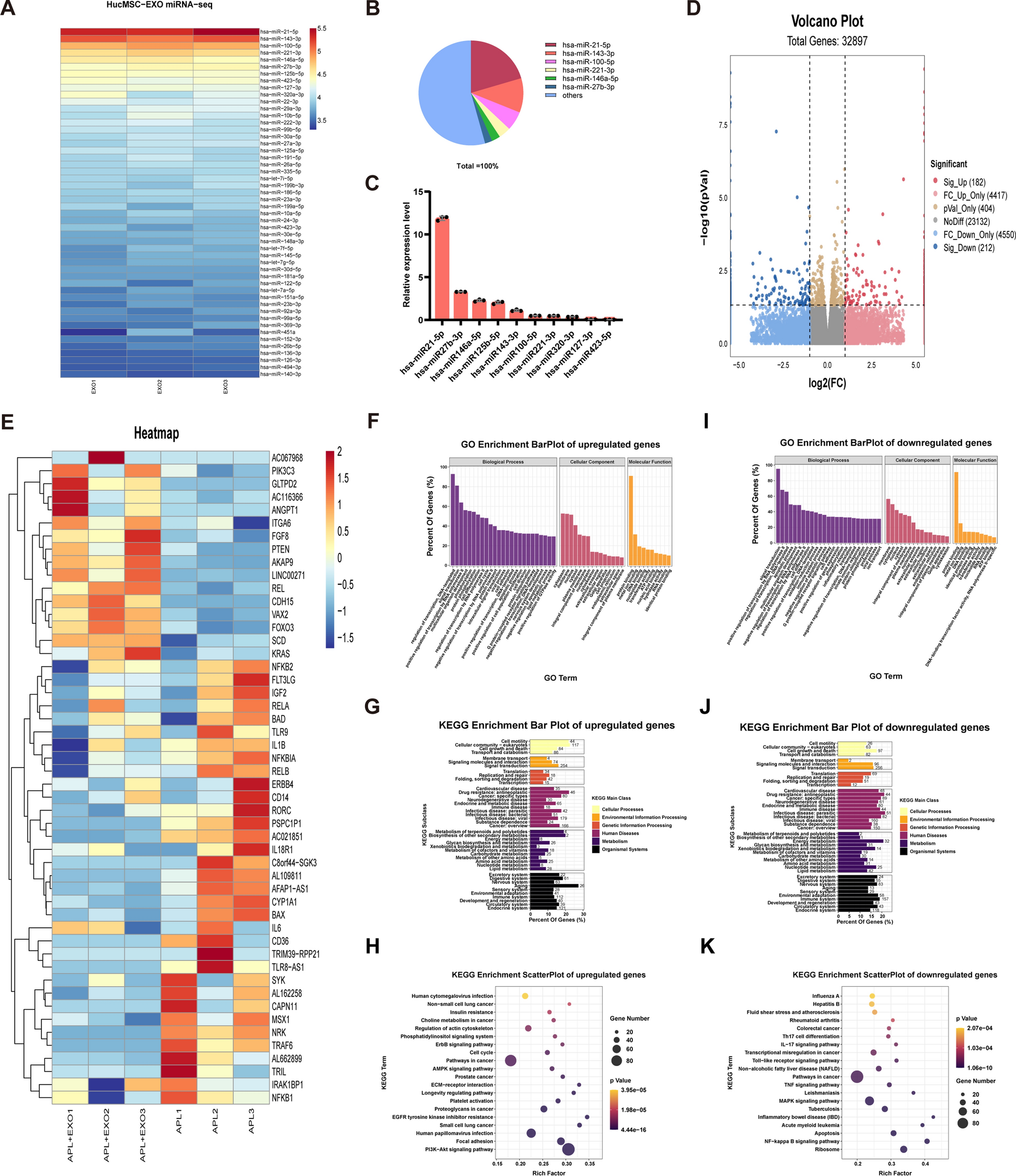
A Heatmap of the top 50 most-enriched miRNAs expressed in hucMSC-exos (n = 3). B Relative percentage of miRNAs in total miRNA reads. C qRT-PCR analyzed the expression levels of the top 10 most-enriched miRNAs in hucMSC–exos (n=3). D Volcano plot of RNA-seq transcriptome data displaying the pattern of the gene expression profile in the HTR8/SVneo cells with or without hucMSC-exos treatment. The aPL + EXO group was incubated with hucMSC-exos (100 ug/ml) for 24 h post aPL stimulation (200 ug/ml). Red and blue dots indicate the significantly up- or down-regulated genes, respectively. p < 0.05, |log2FC|> 1. E Representative heatmap of differentially expressed genes between the aPL + EXO group and aPL group based on the above mRNA-seq data. (Red, relatively upregulated expression; blue, relatively downregulated expression). Each column represents one individual sample, and each row represents one single gene (n = 3). F-K Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis of the up- and down-regulated genes in HTR8/SVneo cells of aPL + EXO group compare with aPL group. Gene percentage refers to the percentage of genes that were significantly enriched in the corresponding secondary class. Rich factor indicates the up-regulated and down-regulated expressed genes divided by the total number of genes. The smaller the p value, the higher enrichment degree. The diameter of the dots indicate the number of genes enriched in the corresponding signal pathways
Lv Qingfeng, Wang Yuan, Tian Wei, Liu Yuqiu, Gu Mengqi, Jiang Xiaotong, Cai Yanjun, Huo Ruiheng, Li Yuchen, Li Lei. (2023) Exosomal miR-146a-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can alleviate antiphospholipid antibody-induced trophoblast injury and placental dysfunction by regulating the TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21(1), 419. [article]
Exosomes originating from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hucMSC-exos) have become a novel strategy for treating various diseases owing to their ability to regulate intercellular signal communication. However, the potential of hucMSC-exos to improve placental injury in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome and its underlying mechanism remain unclear. The objective of this study led by Shandong First Medical University was to explore the potential application of hucMSC-exos in the treatment of obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome and elucidate its underlying mechanism. In this study, hucMSC-exos ameliorated the functional impairment of trophoblasts caused by antiphospholipid antibodies in vitro and attenuated placental dysfunction in mice with obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome by delivering miR-146a-5p. They used LC Sciences’ miRNA microarray service on Total RNA that was extracted from hucMSC-exos. Exosomal miR-146a-5p suppressed the expression of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and inhibited the activation of NF-κB signaling, leading to the down-regulation of IL-1β and IL-18 to rescue inflammation and modulation of Cleaved-CASP3, BAX, and BCL2 to inhibit apoptosis in HTR8/SVneo cells and mice placenta. This study identified the potential molecular basis of how hucMSC-exos improved antiphospholipid antibody-induced placental injury and highlighted the functional importance of the miR-146a-5p/TRAF6 axis in the progression of obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome. More importantly, this study provided a fresh outlook on the promising use of hucMSC-exos as a novel and effective treatment approach in obstetric antiphospholipid syndrome.
MiRNA sequencing analysis of hucMSC-exos and comprehensive analysis of genes and pathways involved in hucMSC-exos treatment based on mRNA high-throughput sequencing
A Heatmap of the top 50 most-enriched miRNAs expressed in hucMSC-exos (n = 3). B Relative percentage of miRNAs in total miRNA reads. C qRT-PCR analyzed the expression levels of the top 10 most-enriched miRNAs in hucMSC–exos (n=3). D Volcano plot of RNA-seq transcriptome data displaying the pattern of the gene expression profile in the HTR8/SVneo cells with or without hucMSC-exos treatment. The aPL + EXO group was incubated with hucMSC-exos (100 ug/ml) for 24 h post aPL stimulation (200 ug/ml). Red and blue dots indicate the significantly up- or down-regulated genes, respectively. p < 0.05, |log2FC|> 1. E Representative heatmap of differentially expressed genes between the aPL + EXO group and aPL group based on the above mRNA-seq data. (Red, relatively upregulated expression; blue, relatively downregulated expression). Each column represents one individual sample, and each row represents one single gene (n = 3). F-K Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes enrichment analysis of the up- and down-regulated genes in HTR8/SVneo cells of aPL + EXO group compare with aPL group. Gene percentage refers to the percentage of genes that were significantly enriched in the corresponding secondary class. Rich factor indicates the up-regulated and down-regulated expressed genes divided by the total number of genes. The smaller the p value, the higher enrichment degree. The diameter of the dots indicate the number of genes enriched in the corresponding signal pathways
Lv Qingfeng, Wang Yuan, Tian Wei, Liu Yuqiu, Gu Mengqi, Jiang Xiaotong, Cai Yanjun, Huo Ruiheng, Li Yuchen, Li Lei. (2023) Exosomal miR-146a-5p derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells can alleviate antiphospholipid antibody-induced trophoblast injury and placental dysfunction by regulating the TRAF6/NF-κB axis. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21(1), 419. [article]