Despite being a common malignant tumor, the molecular mechanism underlying the initiation and progression of triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) remain unclear. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are often polarized into a pro-tumor phenotype and are associated with a poor prognosis of TNBCs. Exosomes, important mediators of cell-cell communication, can be actively secreted by donor cells to reprogram recipient cells. The functions and molecular mechanisms of tumor cell-derived exosomes in TNBCs progression and TAMs reprogramming urgently need to be further explored. In this study led by Zhejiang University, they demonstrated that tumor cell-derived exosomes enriched with miR-184-3p were taken up by macrophages to inhibit JNK signaling pathway by targeting EGR1, thereby inducing M2 polarization of macrophages and synergistically promoting tumor progression. They used LC Sciences’ RNA Sequencing and miRNA Sequencing services on Total RNA that was extracted from M0 macrophages and M0-T-exo. Nanoparticles loaded with oncogene c-Myc inhibitor JQ1 could suppress the polarization process by reducing Rac1-related exosome uptake by macrophage. More importantly, it was found for the first time that tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p was actively sorted into exosomes by binding to RNA-binding protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2B1 (hnRNPA2B1), thus facilitating tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by relieving the inhibitory effect of miR-184-3p on Mastermind-like 1 (MAML1). Overexpressing miR-184-3p in tumor cells and simultaneously knocking down hnRNPA2B1 to block its secretion through exosomes could effectively inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. Their study revealed that hnRNPA2B1-mediated exosomal transfer of tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p from breast cancer cells to macrophages was an important mediator of TNBCs progression, providing new insights into TNBCs pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.
Exosomal miR-184-3p induced M2 macrophage polarization by inhibiting EGR1 expression and JNK signaling pathway
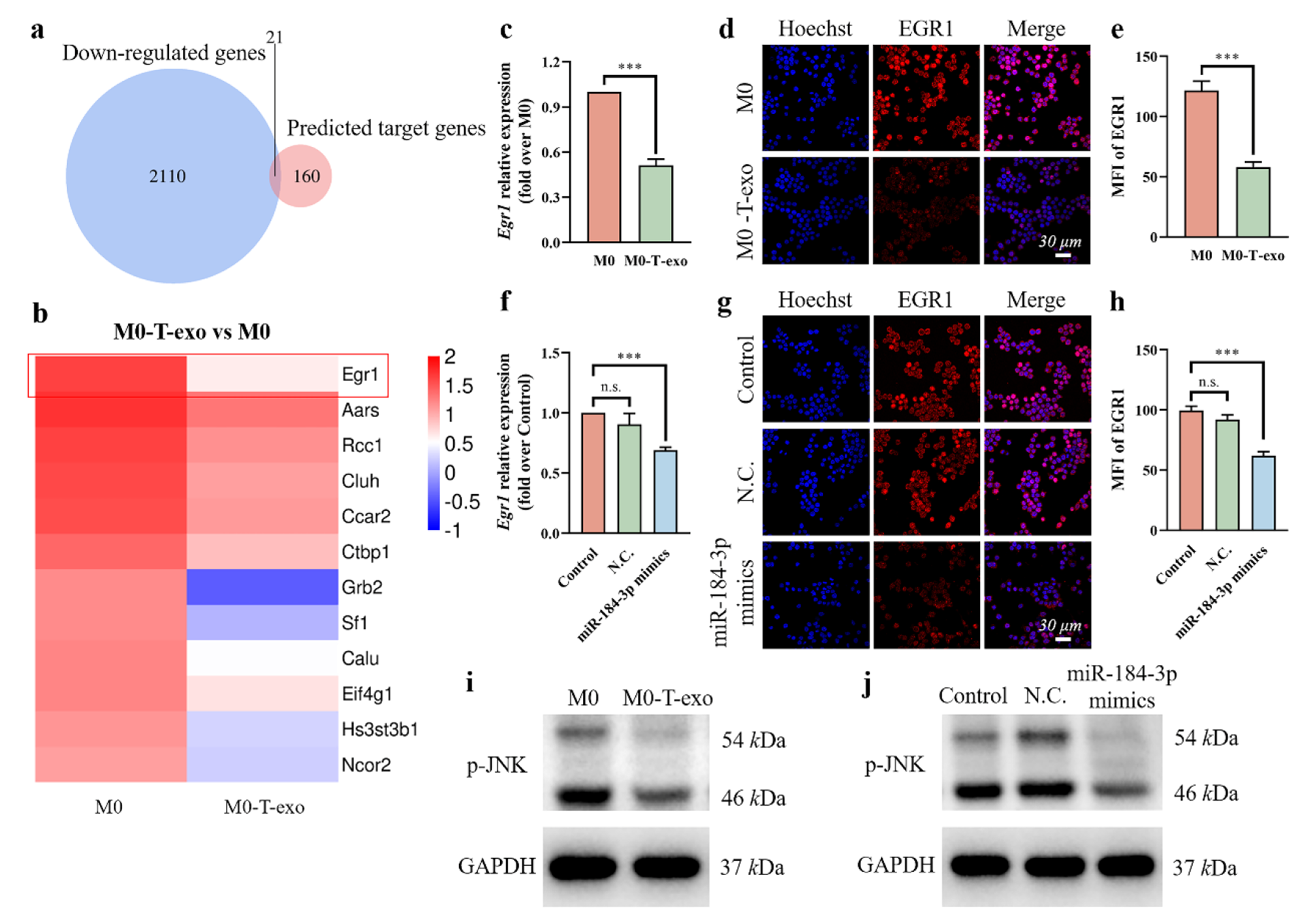
a Venn diagram showed the overlap of mRNAs in down-regulated genes in M0-T-exo detected by mRNA-seq and the predicted target genes of miR-184-3p. b Heatmap of 12 mRNAs screened from (a). c The expression of Egr1 gene in M0-T-exo and M0 macrophages detected by qRT-PCR. d The expression of EGR1 protein in M0-T-exo and M0 macrophages determined by IF staining. Cell nuclei were blue. Rac1 was red. e MFI of Rac1 in (d) calculated by ImageJ software. f The expression of Egr1 gene in macrophages transfected with N.C. or miR-184-3p mimics detected by qRT-PCR. g The expression of EGR1 protein in macrophages transfected with N.C. or miR-184-3p mimics determined by IF staining. Cell nuclei were blue. Rac1 was red. h MFI of Rac1 in (g) calculated by ImageJ software. Western blot assays for p-JNK expression in M0-T-exo (i) and macrophages transfected with miR-184-3p mimics (j). Data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3, ***p < 0.001)
Zhou Xueqing, Hong Yiling, Liu Yupeng, Wang Li, Liu Xuan, Li Yi, Yuan Hong, Hu Fuqiang. (2023) Intervening in hnRNPA2B1-mediated exosomal transfer of tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p for tumor microenvironment regulation and cancer therapy. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21(1), 422. [article]
Despite being a common malignant tumor, the molecular mechanism underlying the initiation and progression of triple-negative breast cancers (TNBCs) remain unclear. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are often polarized into a pro-tumor phenotype and are associated with a poor prognosis of TNBCs. Exosomes, important mediators of cell-cell communication, can be actively secreted by donor cells to reprogram recipient cells. The functions and molecular mechanisms of tumor cell-derived exosomes in TNBCs progression and TAMs reprogramming urgently need to be further explored. In this study led by Zhejiang University, they demonstrated that tumor cell-derived exosomes enriched with miR-184-3p were taken up by macrophages to inhibit JNK signaling pathway by targeting EGR1, thereby inducing M2 polarization of macrophages and synergistically promoting tumor progression. They used LC Sciences’ RNA Sequencing and miRNA Sequencing services on Total RNA that was extracted from M0 macrophages and M0-T-exo. Nanoparticles loaded with oncogene c-Myc inhibitor JQ1 could suppress the polarization process by reducing Rac1-related exosome uptake by macrophage. More importantly, it was found for the first time that tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p was actively sorted into exosomes by binding to RNA-binding protein heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2B1 (hnRNPA2B1), thus facilitating tumor cell proliferation and metastasis by relieving the inhibitory effect of miR-184-3p on Mastermind-like 1 (MAML1). Overexpressing miR-184-3p in tumor cells and simultaneously knocking down hnRNPA2B1 to block its secretion through exosomes could effectively inhibit tumor growth and metastasis. Their study revealed that hnRNPA2B1-mediated exosomal transfer of tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p from breast cancer cells to macrophages was an important mediator of TNBCs progression, providing new insights into TNBCs pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies.
Exosomal miR-184-3p induced M2 macrophage polarization by inhibiting EGR1 expression and JNK signaling pathway
a Venn diagram showed the overlap of mRNAs in down-regulated genes in M0-T-exo detected by mRNA-seq and the predicted target genes of miR-184-3p. b Heatmap of 12 mRNAs screened from (a). c The expression of Egr1 gene in M0-T-exo and M0 macrophages detected by qRT-PCR. d The expression of EGR1 protein in M0-T-exo and M0 macrophages determined by IF staining. Cell nuclei were blue. Rac1 was red. e MFI of Rac1 in (d) calculated by ImageJ software. f The expression of Egr1 gene in macrophages transfected with N.C. or miR-184-3p mimics detected by qRT-PCR. g The expression of EGR1 protein in macrophages transfected with N.C. or miR-184-3p mimics determined by IF staining. Cell nuclei were blue. Rac1 was red. h MFI of Rac1 in (g) calculated by ImageJ software. Western blot assays for p-JNK expression in M0-T-exo (i) and macrophages transfected with miR-184-3p mimics (j). Data were expressed as mean ± SD (n = 3, ***p < 0.001)
Zhou Xueqing, Hong Yiling, Liu Yupeng, Wang Li, Liu Xuan, Li Yi, Yuan Hong, Hu Fuqiang. (2023) Intervening in hnRNPA2B1-mediated exosomal transfer of tumor-suppressive miR-184-3p for tumor microenvironment regulation and cancer therapy. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 21(1), 422. [article]