Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic recurrent disease that can be controlled by various natural extracts. Anthocyanins (ANCs) from bilberry have significant antioxidant capacity and are widely used as food colors and antioxidants. In this study conducted by China Jiliang University, they investigated the protective effects of bilberry anthocyanin extracts (BANCs) against dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced intestinal inflammation in a Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster) model, and the effects on the lifespan, antioxidant capacity, intestinal characteristics, and microbiome and gene expression profiles were analyzed to elucidate the underlying biological mechanisms. In DSS-induced normal and axenic D. melanogaster, BANCs significantly increased the survival rate, maintained the intestinal morphology and integrity, and reduced the number of dead intestinal epithelial cells and the ROS level of these cells. They used LC Sciences’ 16S rRNA sequencing service to analyze the D. melanogaster intestinal microbial composition. BANC supplementation had no significant effect on the intestinal microflora of DSS-induced D. melanogaster, as demonstrated by a 16S rDNA analysis, but improved the antioxidant capacity by activating the relative gene expression of NRF2 signaling pathways in the intestine of D. melanogaster with DSS-induced inflammation. Therefore, the results demonstrate that BANCs effectively alleviate intestinal inflammatory injury induced by DSS and improve the antioxidant capacity of D. melanogaster by modulating NRF2 signaling pathways, and could thus promote the application of BANCs as functional foods.
Effects of BANCs on the DSS-induced female D. melanogaster intestinal microbiota
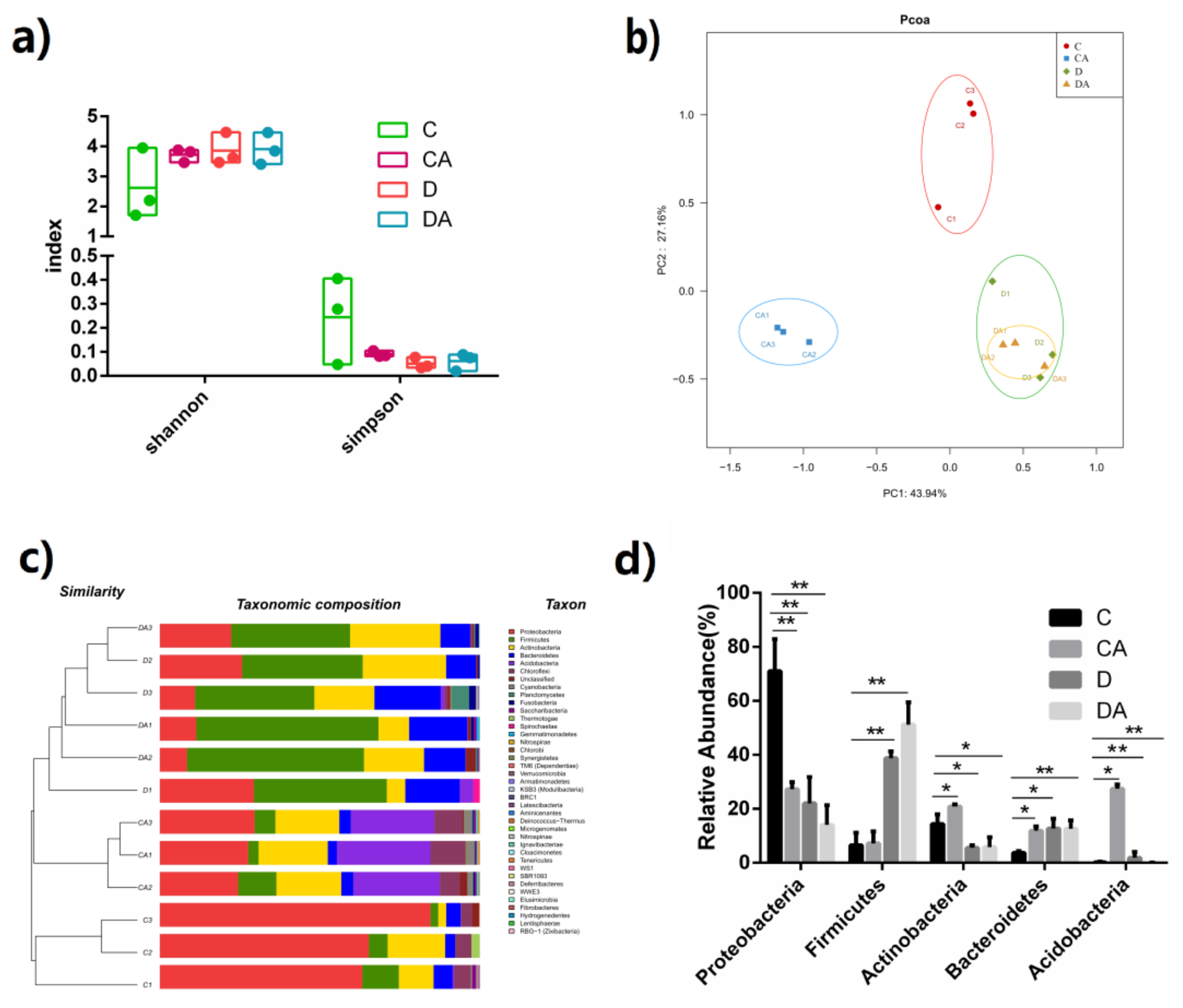
C, CA, D, and DA represent the blank control group, BANC control group, inflamed group, and BANCs + inflamed group, respectively. (a) Effect of BANCs on the α-diversity (Shannon and Simpson index) of the midgut microbiota of DSS-exposed D. melanogaster. The p value of all the groups was obtained by the Kruskal–Wallis test. (b) Effect of BANCs on the β-diversity of the midgut microbiota of DSS-exposed D. melanogaster and PCoA based on weighted UniFrac distance. (c) Bacterial taxonomic profiling of the four groups at the phylum level (n = 3). (d) Relative abundances of five intestinal microorganisms in DSS-induced D. melanogaster at the phylum level. The results are presented as the means ± SEMs (n = 3); statistical comparisons were performed with t tests. Statistical significance: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Zhang G, Gu Y, Dai X. (2022) Protective Effect of Bilberry Anthocyanin Extracts on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Intestinal Damage in Drosophila melanogaster. Nutrients 14(14), 2875. [article]
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a chronic recurrent disease that can be controlled by various natural extracts. Anthocyanins (ANCs) from bilberry have significant antioxidant capacity and are widely used as food colors and antioxidants. In this study conducted by China Jiliang University, they investigated the protective effects of bilberry anthocyanin extracts (BANCs) against dextran sulphate sodium (DSS)-induced intestinal inflammation in a Drosophila melanogaster (D. melanogaster) model, and the effects on the lifespan, antioxidant capacity, intestinal characteristics, and microbiome and gene expression profiles were analyzed to elucidate the underlying biological mechanisms. In DSS-induced normal and axenic D. melanogaster, BANCs significantly increased the survival rate, maintained the intestinal morphology and integrity, and reduced the number of dead intestinal epithelial cells and the ROS level of these cells. They used LC Sciences’ 16S rRNA sequencing service to analyze the D. melanogaster intestinal microbial composition. BANC supplementation had no significant effect on the intestinal microflora of DSS-induced D. melanogaster, as demonstrated by a 16S rDNA analysis, but improved the antioxidant capacity by activating the relative gene expression of NRF2 signaling pathways in the intestine of D. melanogaster with DSS-induced inflammation. Therefore, the results demonstrate that BANCs effectively alleviate intestinal inflammatory injury induced by DSS and improve the antioxidant capacity of D. melanogaster by modulating NRF2 signaling pathways, and could thus promote the application of BANCs as functional foods.
Effects of BANCs on the DSS-induced female D. melanogaster intestinal microbiota
C, CA, D, and DA represent the blank control group, BANC control group, inflamed group, and BANCs + inflamed group, respectively. (a) Effect of BANCs on the α-diversity (Shannon and Simpson index) of the midgut microbiota of DSS-exposed D. melanogaster. The p value of all the groups was obtained by the Kruskal–Wallis test. (b) Effect of BANCs on the β-diversity of the midgut microbiota of DSS-exposed D. melanogaster and PCoA based on weighted UniFrac distance. (c) Bacterial taxonomic profiling of the four groups at the phylum level (n = 3). (d) Relative abundances of five intestinal microorganisms in DSS-induced D. melanogaster at the phylum level. The results are presented as the means ± SEMs (n = 3); statistical comparisons were performed with t tests. Statistical significance: * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
Zhang G, Gu Y, Dai X. (2022) Protective Effect of Bilberry Anthocyanin Extracts on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Intestinal Damage in Drosophila melanogaster. Nutrients 14(14), 2875. [article]