N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays important roles in bioprocesses and diseases. AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) is one of two m6A demethylases. In this study led by Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, they reveal that ALKBH5 is acetylated at lysine 235 (K235) by lysine acetyltransferase 8 and deacetylated by histone deacetylase 7. They used LC Sciences’ m6A RNA sequencing service on total RNA extracted from cells and tissue samples. K235 acetylation strengthens the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 by increasing its recognition of m6A on mRNA. RNA-binding protein paraspeckle component 1 (PSCP1) is a regulatory subunit of ALKBH5 and preferentially interacts with K235-acetylated ALKBH5 to recruit and facilitate the recognition of m6A mRNA by ALKBH5, thereby promoting m6A erasure. Mitogenic signals promote ALKBH5 K235 acetylation. K235 acetylation of ALKBH5 is upregulated in cancers and promotes tumorigenesis. Thus, their findings reveal that the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 is orchestrated by its K235 acetylation and regulatory subunit PSPC1 and that K235 acetylation is necessary for the m6A demethylase activity and oncogenic roles of ALKBH5.
ALKBH5 acetylation at K235 is critical for the RNA m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5
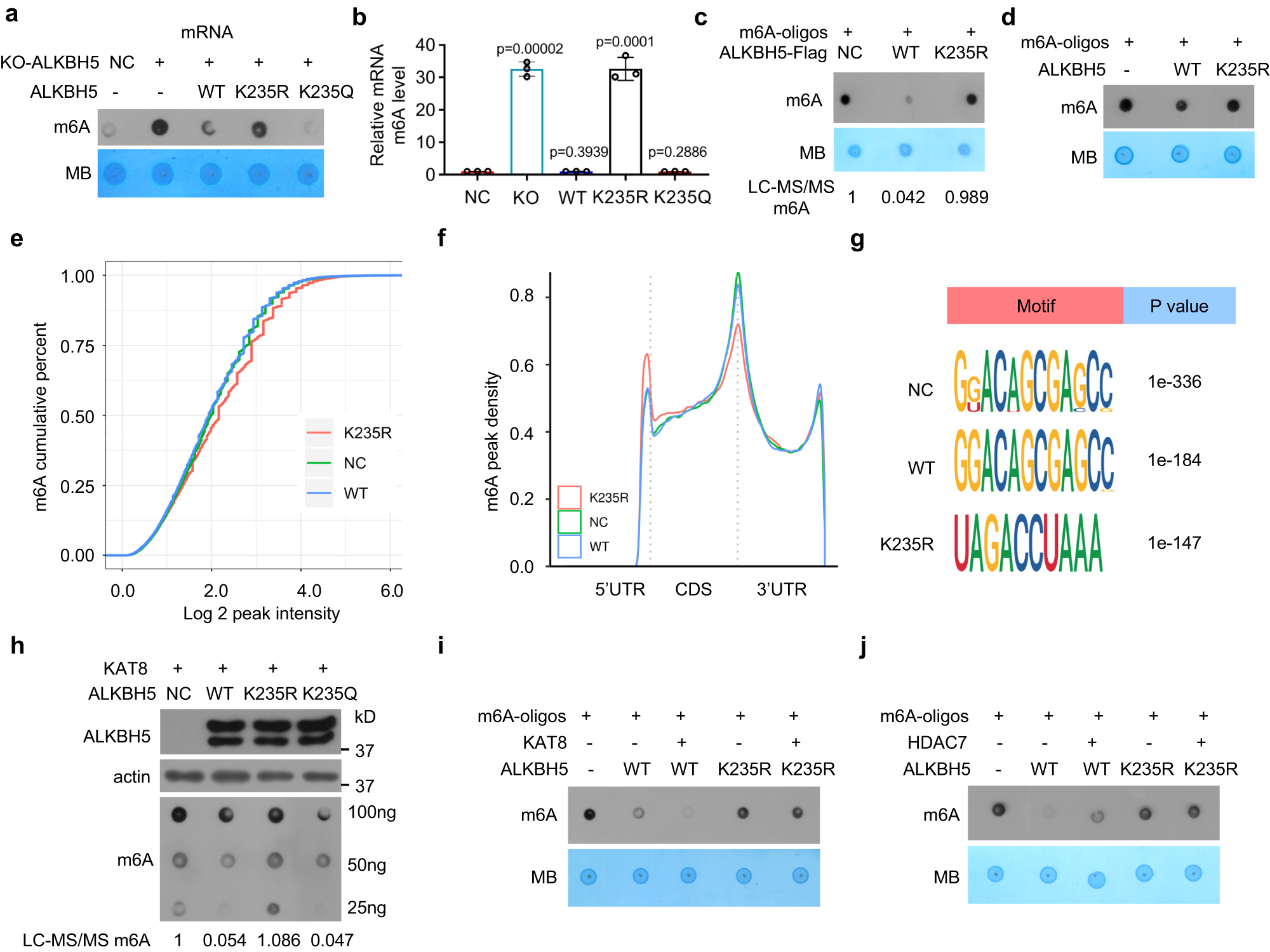
a, b K235 acetylation of ALKBH5 decreased the cellular mRNA m6A levels. The wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R and K235Q plasmids were transfected into ALKBH5 KO HeLa cells, and the cellular mRNA m6A level was determined by dot blotting (a) and quantified by LC‒MS/MS analysis (b) (n = 3, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, mean ± SD). c, d Wild-type ALKBH5, but not the K235R mutant, directly demethylated m6A in the m6A-RNA oligos in the in vitro demethylation reaction. Immunopurified wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R (c) or recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R (d) were incubated with m6A RNA oligos; the m6A level was determined by dot blotting or LC‒MS/MS assays. e Cumulative distribution curve for the m6A peak abundance in NC, WT and K235R cells. f Distribution of m6A peaks in the 5′ UTR, CDS, stop codon and 3′ UTR in NC, WT and K235R cells. g Top consensus motif identified by HOMER with m6A peaks in NC, WT and K235R cells. h The indicated ALKBH5 vectors together with the KAT8 plasmid were cotransfected into ALKBH5 KO HeLa cells, and the cellular RNA m6A level was determined. i, j Recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 or its K235R mutant was incubated with m6A RNA oligos after recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 or its K235R mutant was treated with immunopurified KAT8 (i) or immunopurified HDAC7 (j), and the m6A level was determined. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Zhang Xiao-Lan, Chen Xin-Hui, Xu Binwu, Chen Min, Zhu Song, Meng Nan, Wang Ji-Zhong, Zhu Huifang, Chen De, Liu Jin-Bao, Yan Guang-Rong. (2023) K235 acetylation couples with PSPC1 to regulate the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 and tumorigenesis. Nature Communications 14(1), 3815. [article]
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays important roles in bioprocesses and diseases. AlkB homolog 5 (ALKBH5) is one of two m6A demethylases. In this study led by Third Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, they reveal that ALKBH5 is acetylated at lysine 235 (K235) by lysine acetyltransferase 8 and deacetylated by histone deacetylase 7. They used LC Sciences’ m6A RNA sequencing service on total RNA extracted from cells and tissue samples. K235 acetylation strengthens the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 by increasing its recognition of m6A on mRNA. RNA-binding protein paraspeckle component 1 (PSCP1) is a regulatory subunit of ALKBH5 and preferentially interacts with K235-acetylated ALKBH5 to recruit and facilitate the recognition of m6A mRNA by ALKBH5, thereby promoting m6A erasure. Mitogenic signals promote ALKBH5 K235 acetylation. K235 acetylation of ALKBH5 is upregulated in cancers and promotes tumorigenesis. Thus, their findings reveal that the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 is orchestrated by its K235 acetylation and regulatory subunit PSPC1 and that K235 acetylation is necessary for the m6A demethylase activity and oncogenic roles of ALKBH5.
ALKBH5 acetylation at K235 is critical for the RNA m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5
a, b K235 acetylation of ALKBH5 decreased the cellular mRNA m6A levels. The wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R and K235Q plasmids were transfected into ALKBH5 KO HeLa cells, and the cellular mRNA m6A level was determined by dot blotting (a) and quantified by LC‒MS/MS analysis (b) (n = 3, two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test, mean ± SD). c, d Wild-type ALKBH5, but not the K235R mutant, directly demethylated m6A in the m6A-RNA oligos in the in vitro demethylation reaction. Immunopurified wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R (c) or recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 and its mutant K235R (d) were incubated with m6A RNA oligos; the m6A level was determined by dot blotting or LC‒MS/MS assays. e Cumulative distribution curve for the m6A peak abundance in NC, WT and K235R cells. f Distribution of m6A peaks in the 5′ UTR, CDS, stop codon and 3′ UTR in NC, WT and K235R cells. g Top consensus motif identified by HOMER with m6A peaks in NC, WT and K235R cells. h The indicated ALKBH5 vectors together with the KAT8 plasmid were cotransfected into ALKBH5 KO HeLa cells, and the cellular RNA m6A level was determined. i, j Recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 or its K235R mutant was incubated with m6A RNA oligos after recombinant wild-type ALKBH5 or its K235R mutant was treated with immunopurified KAT8 (i) or immunopurified HDAC7 (j), and the m6A level was determined. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Zhang Xiao-Lan, Chen Xin-Hui, Xu Binwu, Chen Min, Zhu Song, Meng Nan, Wang Ji-Zhong, Zhu Huifang, Chen De, Liu Jin-Bao, Yan Guang-Rong. (2023) K235 acetylation couples with PSPC1 to regulate the m6A demethylation activity of ALKBH5 and tumorigenesis. Nature Communications 14(1), 3815. [article]