A mouse- and human-brain-abundant, nuclear factor (NF)-кB-regulated, micro RNA-146a (miRNA-146a) is an important modulator of the innate immune response and inflammatory signaling in specific immunological and brain cell types. Through LC Sciences’ miRNA microarray profiling service, researchers at the LSU Neuroscience Center found levels of miRNA-146a are induced in human brain cells challenged with at least five different species of single- or double-stranded DNA or RNA neurotrophic viruses, suggesting a broad role for miRNA-146a in the brain’s innate immune response and antiviral immunity. Upregulated miRNA-146a is also observed in pro-inflammatory cytokine-, Aβ42 peptide- and neurotoxic metal-induced, oxidatively stressed human neuronal-glial primary cell cocultures, in murine scrapie and in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) brain. In AD, miRNA-146a levels are found to progressively increase with disease severity and co-localize to brain regions enriched in inflammatory neuropathology.
This study provides evidence of upregulation of miRNA-146a in extremely rare (incidence 1–10 per 100 million) human prion-based neurodegenerative disorders, including sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann–Straussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS). The findings suggest that an upregulated miRNA-146a may be integral to innate immune or inflammatory brain cell responses in prion-mediated infections and to progressive and irreversible neurodegeneration of both the murine and human brain.
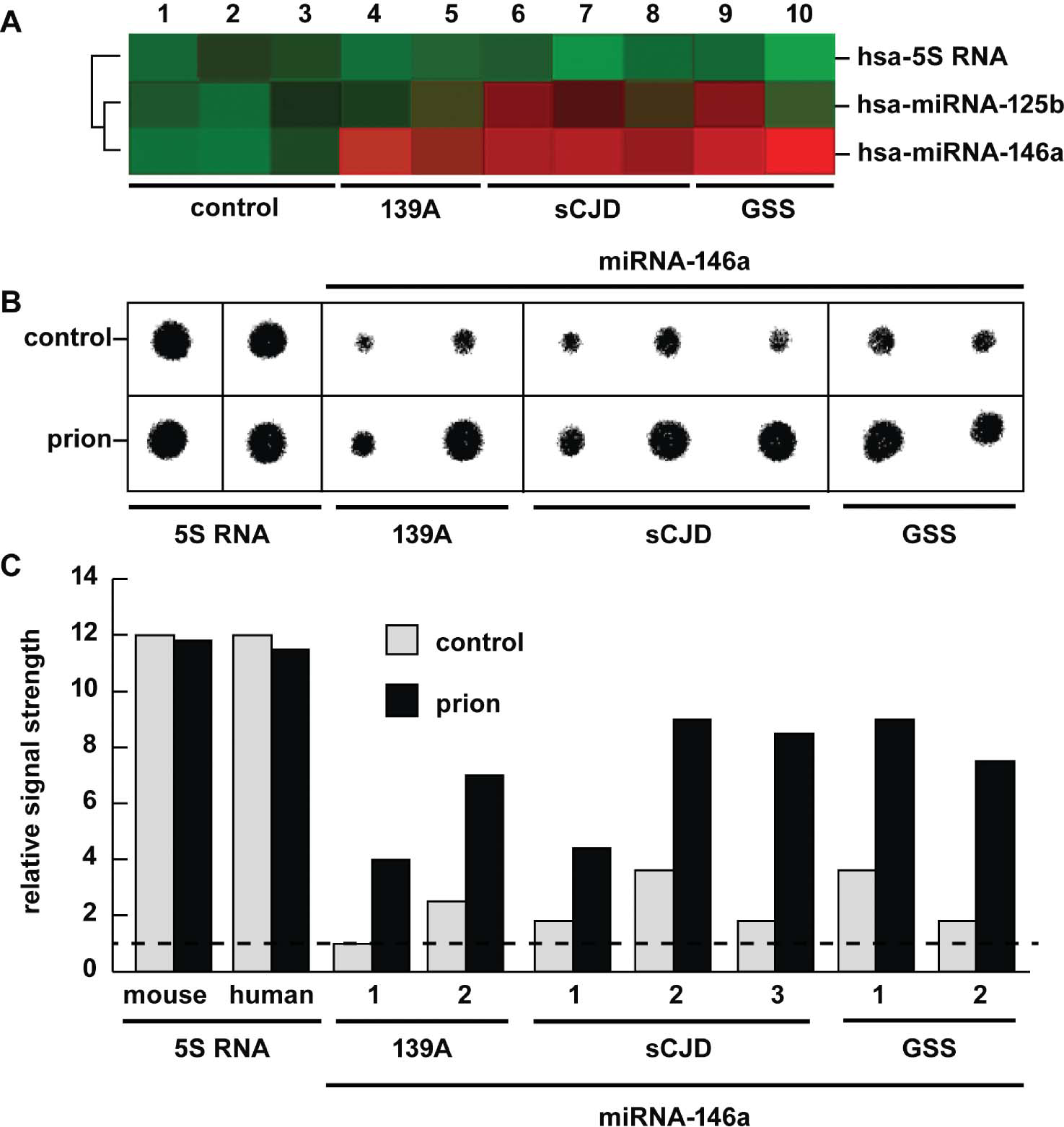
Abundance of hsa-miRNA-125b and/or hsa-miRNA-146a in comparison to an internal control hsa-5S RNA marker in murine scrapie 139a, sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD), and Gerstmann–Straussler–Scheinker syndrome (GSS) compared to age-matched controls (control) in the same brain region as analyzed by (A) fluorescent miRNA array cluster analysis (LC Sciences, Houston TX) and (B) concentrated Northern dot-blot analysis of 5S RNA and miRNA-146a using high-specific-activity radiolabeled probes (Cui et al. 2005; Sethi and Lukiw 2009); (C) quantified results from Northern dot-blot analysis; dashed horizontal line indicates control 139A levels relative to 5S RNA for ease of comparison. In (A) panel 1 is the age-matched control for murine 139a (n = 2; lanes 4 and 5); lanes 2 and 3 are the mean age-matched control for the individual cases for sCJD (n = 3; lanes 6–8) and GSS (n = 2, lanes 9 and 10), respectively; by convention, green colors indicate no change and red colors indicate upregulation (LC Sciences; Lukiw et al. 2008). Squared black lines to the left of panel (A) indicate that a mean signal intensity comparison between hsa-5S-RNA and hsa-miRNA-125b yielded a significance of p > .07 (ANOVA), and between 5S-RNA and hsa-miRNA-146a yielded a p < .01 (ANOVA). miRNA-125b was found to be significantly upregulated in one of two GSS cases and two of three CJD cases; miRNA-146a was found to be consistently elevated in all sCJD or GSS cases using miRNA array analysis; and this was further confirmed using quantitative Northern dot blot analysis (B and C). The 22 nucleotide hsa-5S-RNA probe was derived from the 5 end of the 107 nucleotide human 5S ribosomal RNA (5S RNA) and in panel (B) was loaded at 1/10 the concentration of miRNA-146a (Sethi and Lukiw 2009) (color figure available online).
Related Service
miRNA Microarray Service – LC Sciences provides a microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling service using microarrays based on our in-house developed µParaflo® technology platform. We have standard arrays for all mature miRNAs of all species available in the latest version of the miRBase database (Release 21, July 2014). Our service is comprehensive and includes sample labeling, array hybridization, image data processing and in-depth data analysis. Two-three weeks after receiving your total RNA samples, we’ll send you both the raw and fully analyzed data. [Learn more…]
Reference
Lukiw WJ, Dua P, Pogue AI, Eicken C, Hill JM. (2011) “Upregulation of Micro RNA-146a (miRNA-146a), A Marker for Inflammatory Neurodegeneration, in Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker (GSS) Syndrome”. J Toxicol Environ Health A 74(22-24), 1460-8. [abstract]
