Pathologic conditions in the central nervous system, regardless of the underlying injury mechanism, show a certain level of blood–brain barrier (BBB) impairment. Endothelial dysfunction is the earliest event in the initiation of vascular damage caused by inflammation due to stroke, atherosclerosis, trauma, or brain infections. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as a class of gene expression regulators, but the relationship between neuroinflammation and miRNA expression in brain endothelium remains unexplored. Previously, researchers from Temple University showed the BBB-protective and anti-inflammatory effects of glycogen synthase kinase (GSK) 3β inhibition in brain endothelium in in vitro and in vivo models of neuroinflammation. In their recent study, they used LC Sciences’ miRNA microarray service to identify miRNAs induced in primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells after exposure to the pro-inflammatory cytokine, tumor necrosis factor-α, with/out GSK3β inhibition.
Among the highly modified miRNAs, let-7 and miR-98 were predicted to target the inflammatory molecules, CCL2 and CCL5. Overexpression of let-7 and miR-98 in vitro and in vivo resulted in reduced leukocyte adhesion to and migration across endothelium, diminished expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increased BBB tightness, attenuating barrier ‘leakiness’ in neuroinflammation conditions. This work is the first of it’s kind to show that miRNAs can be used as a therapeutic tool to prevent the BBB dysfunction in neuroinflammation.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) differentially expressed in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNFα)-treated cells compared with nontreated cells
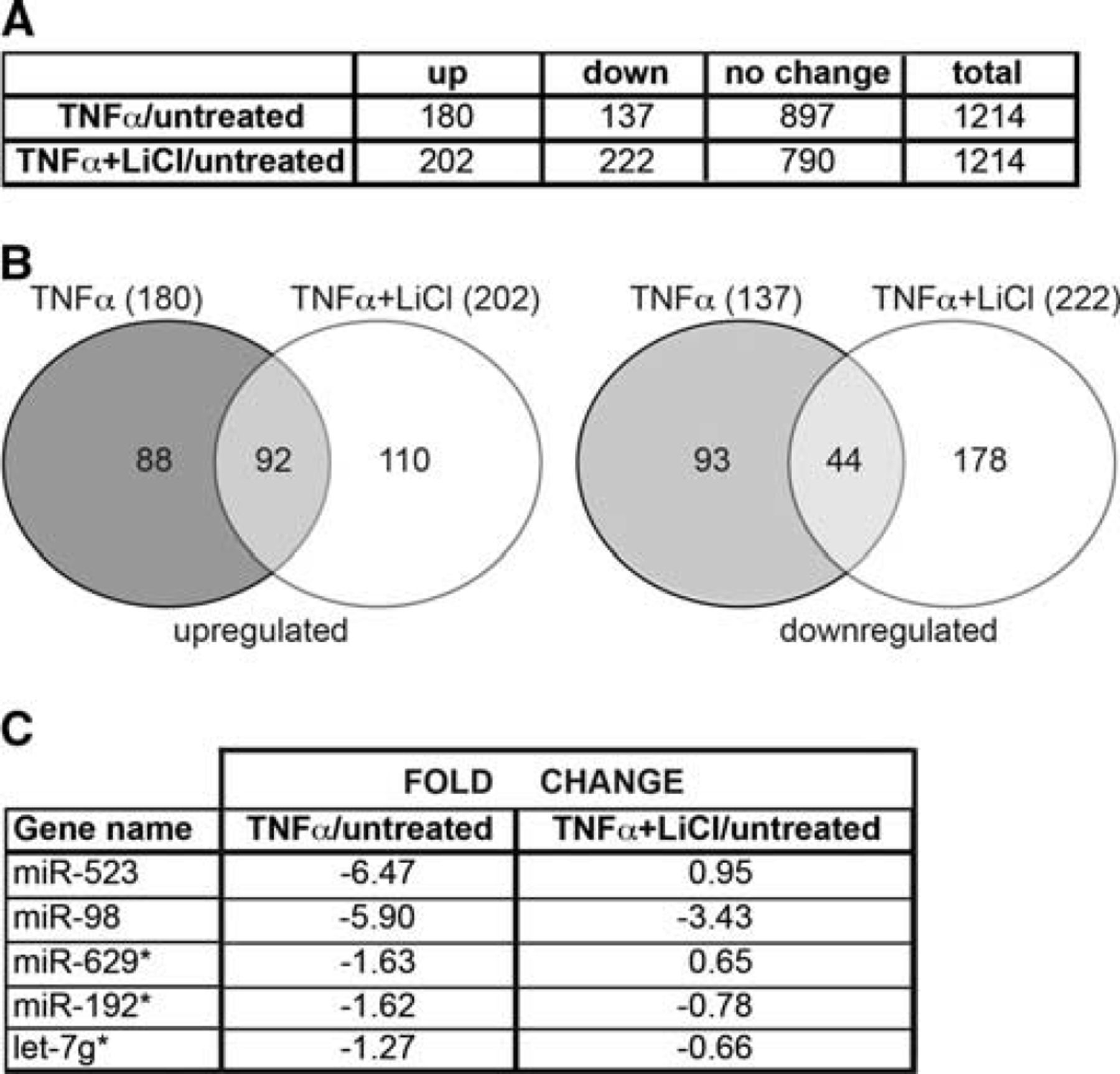
(A) Upregulated and downregulated genes obtained by microarray analysis. Data represent genes with fold change of −1 < or >1 (P>0.01). (B) Venn diagram shows possible relations among the treatments. (C) miRNA gene expression changed significantly (P>0.01) after treatment with lithium chloride (LiCl).
Related Service
miRNA Microarray Service – LC Sciences provides a microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling service using microarrays based on our in-house developed µParaflo® technology platform. We have standard arrays for all mature miRNAs of all species available in the latest version of the miRBase database (Release 21, July 2014). Our service is comprehensive and includes sample labeling, array hybridization, image data processing and in-depth data analysis. Two-three weeks after receiving your total RNA samples, we’ll send you both the raw and fully analyzed data. [Learn more…]
Reference
Rom S, Dykstra H, Zuluaga-Ramirez V, Reichenbach N. L, Persidsky Y. (2015) miR-98 and let-7g* protect the blood–brain barrier under neuroinflammatory conditions J of Cereb Blood Flow 35(12):1957-65. [abstract]
