Myocardial infarction (MI) is a leading cause of death worldwide. Because endogenous cardiac repair mechanisms are not sufficient for meaningful tissue regeneration, MI results in loss of cardiac tissue and detrimental remodeling events. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression in a sequence dependent manner.
Researchers at miRagen Therapeutics set out to examine whether miRNAs are involved in ischemia-reperfusion injury of the porcine heart. They used LC Sciences’ miRNA microarray service to perform analysis on porcine cardiac samples after ischemia-reperfusion injury and profiled miRNA expression in the infarct and border zone regions post-MI compared with control tissue from sham-operated animals. The data showed a distinct miRNA expression signature and indicated that miRNAs are dynamically regulated in different regions of the porcine heart during post-MI remodeling, which could be confirmed by miRNA-specific real-time PCR analysis.
Their data indicate that the miR-15 family, which includes 6 closely related miRNAs, is regulated in the infarcted region of the heart in response to ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice and pigs. LNA-modified chemistries can effectively silence miR-15 family members in vitro and render cardiomyocytes resistant to hypoxia-induced cardiomyocyte cell death. Correspondingly, systemic delivery of miR-15 anti-miRs dose-dependently represses miR-15 in cardiac tissue of both mice and pigs, whereas therapeutic targeting of miR-15 in mice reduces infarct size and cardiac remodeling and enhances cardiac function in response to MI.
miR-15 inhibition reduces infarct size and improves function in response to ischemia
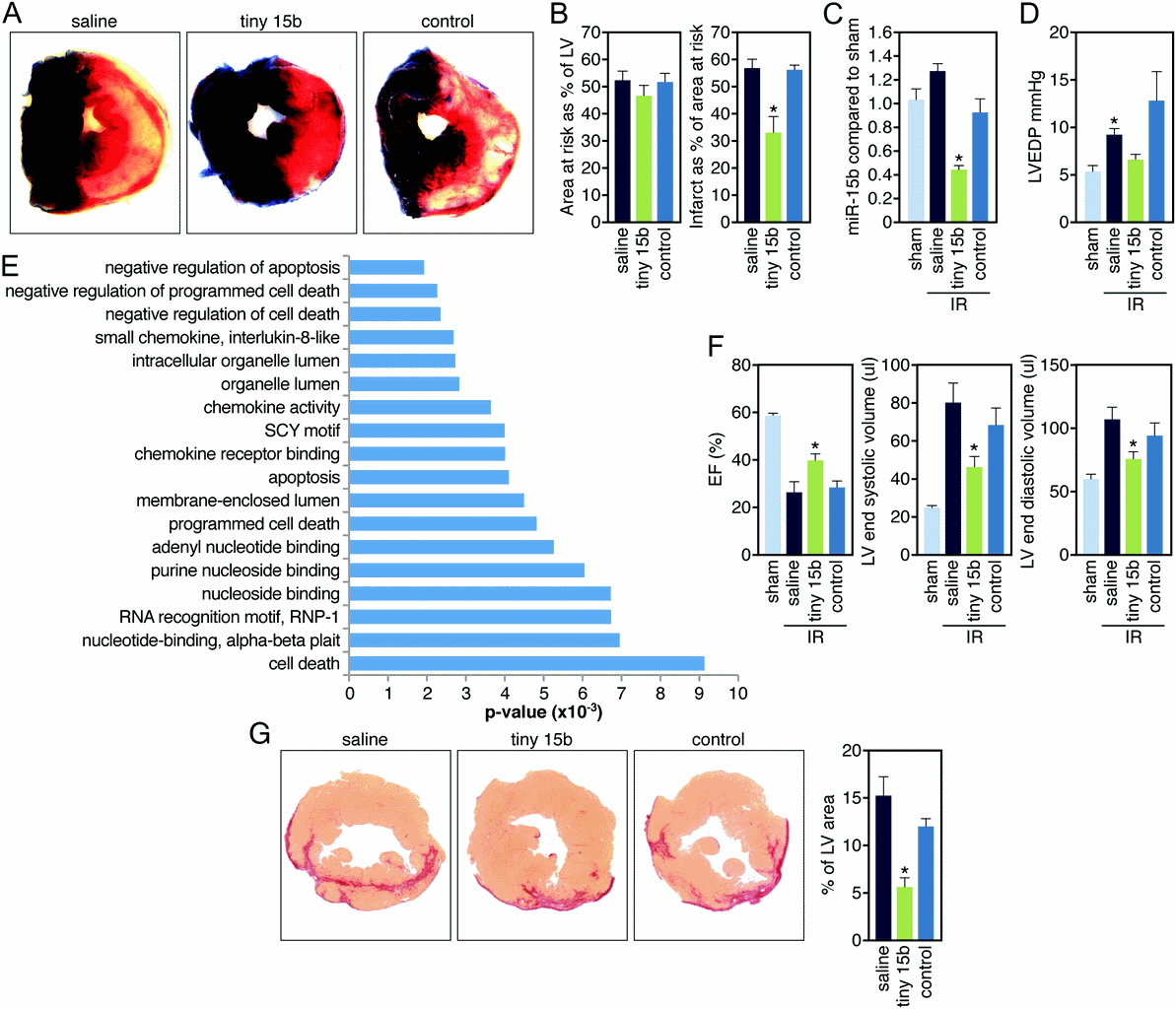
A, Representative images after TTC staining indicate that although the area at risk (AAR, red and white) is comparable between the different treatment groups, the infarcted area (IA, white) is smaller in the tiny 15b–treated animals (control indicates control oligonucleotide). B, Quantification of cross sections of the infarcted hearts indicate that the AAR is [almost equal to]50% of the LV for all 3 treatment groups, whereas administration of 0.5 mg/kg of tiny 15b during reperfusion results in a significant reduction in infarct size compared with either saline or control oligo (*P<0.05 versus saline and control by ANOVA; control indicates control oligonucleotide). C, Real-time PCR analysis on tissue of the ischemic region 24 hours after reperfusion indicates inhibition of miR-15b in response to tiny 15b treatment (*P<0.05 versus saline and control oligonucleotide treated by ANOVA). D, Left ventricular end-diastolic pressure recordings 24 hours after reperfusion reveals an increase with saline treatment and a reduction with tiny 15b treatment (control indicates control oligonucleotide, *P<0.05 versus sham Kruskal-Wallis test). E, Ontology analysis of transcripts upregulated >=1.5-fold in the ischemic region of hearts 24 hours after reperfusion treated with tiny 15b treatment compared with saline, based on microarray profiling. Negative regulators of apoptosis and cell death are significantly overrepresented. F, Echocardiography shows a reduction in ejection fraction (EF) and increases in LV volumes 2 weeks after infarct, all of which are significantly improved in response to tiny 15b treatment (*P<0.05 versus saline and control by ANOVA for EF and LVESV, versus saline only LVEDV; sham indicates no ischemia/reperfusion; control, control oligo). G, Representative images of Picrosirius red–stained cross sections demonstrate a reduction in collagen content of the left ventricle 2 weeks after reperfusion with tiny 15b treatment. Quantification of fibrosis as a percentage of total left ventricular area reveals a statistically significant reduction in the tiny 15b–treated group (*P<0.05 versus saline-treated by ANOVA). LV indicates left ventricle.
Related Service
miRNA Microarray Service – LC Sciences provides a microRNA (miRNA) expression profiling service using microarrays based on our in-house developed µParaflo® technology platform. We have standard arrays for all mature miRNAs of all species available in the latest version of the miRBase database (Release 21, July 2014). Our service is comprehensive and includes sample labeling, array hybridization, image data processing and in-depth data analysis. Two-three weeks after receiving your total RNA samples, we’ll send you both the raw and fully analyzed data. [Learn more…]
Reference
Hullinger TG, Montgomery RL, Seto AG, Dickinson BA, Semus HM, Lynch JM, Dalby CM, Robinson K, Stack C, Latimer PA, Hare JM, Olson EN, van Rooij E. (2011) Inhibition of miR-15 Protects Against Cardiac Ischemic Injury. Circ Res 110(1):71-81. [abstract]
