MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes (T2D); they regulate several metabolic pathways including insulin secretion, glucose homeostasis, so their potential as biomarkers of diagnosis and prognosis has became increasingly appreciated. In this study, researchers from the Hangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention explore serum miRNA profiles in T2D patients. A total of ten candidate miRNAs were identified by LC Sciences’ miRNA Sequencing and followed by a stem-loop quantitative reverse transcription PCR (qRT-PCR) to assess these candidate serum miRNAs. The results of qRT-PCR assessment revealed low serum levels of miR-23a, let-7i, miR-486, miR-96, miR-186, miR-191, miR-192, and miR-146a in T2D. Except for significantly lower in T2D and pre-diabetes patients compared with normal glucose tolerance (NGT) controls (P = 2.87E−05 and P = 3.75E−02), the levels of miR-23a demonstrated also significant decline in T2D patients compared with pre-diabetes patients (P = 1.06E−02). This marker yielded an AUC of 0.835 (95 % CI 0.717–0.954). At a cutoff value of 1.645, the sensitivity was 79.2 % and the specificity was 75.0 % in discriminating T2D patients from NGT normal controls. These results revealed that serum miR-23a was a valuable biomarker for early detection of T2D and pre-diabetes with NGT.
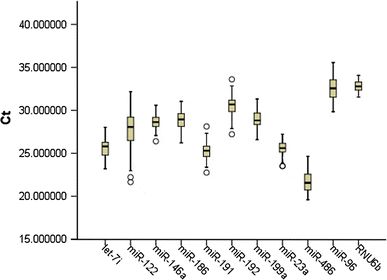
Threshold cycle (Ct) values of all ten miRNAs and RNU6B
Related Service
miRNA Sequencing Services – High-throughput sequencing is now available in addition to existing microarray and qRT-PCR profiling services for the most complete picture of miRNA expression in your samples. miRNA sequencing is a new method and a powerful tool to identify and quantitatively decode the entire population of miRNAs in your sample. [Learn more…]
Reference
Yang Z, Chen H, Si H, Li X, Ding X, Sheng Q, Chen P, Zhang H. (2014) Serum miR-23a, a potential biomarker for diagnosis of pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol 51(5):823-31. [abstract]
