Intermuscular adipose tissue is located between the muscle fiber bundles in skeletal muscles, and has similar metabolic features to visceral adipose tissue, which has been found to be related to a number of obesity-related diseases. Although various miRNAs are known to play crucial roles in adipose deposition and adipogenesis, the microRNA transcriptome of intermuscular adipose tissue has not, until now, been studied.
Here, researchers at the Sichuan Agricultural University utilized LC Sciences’ service to sequence the miRNA transcriptomes of porcine intermuscular adipose tissue by small RNA-sequencing and compared it to a representative subcutaneous adipose tissue. We found that the inflammation- and diabetes-related miRNAs were significantly enriched in the intermuscular rather than in the subcutaneous adipose tissue. A functional enrichment analysis of the genes predicted to be targeted by the enriched miRNAs also indicated that intermuscular adipose tissue was associated mainly with immune and inflammation responses. Our results suggest that the intermuscular adipose tissue should be recognized as a potential metabolic risk factor of obesity.
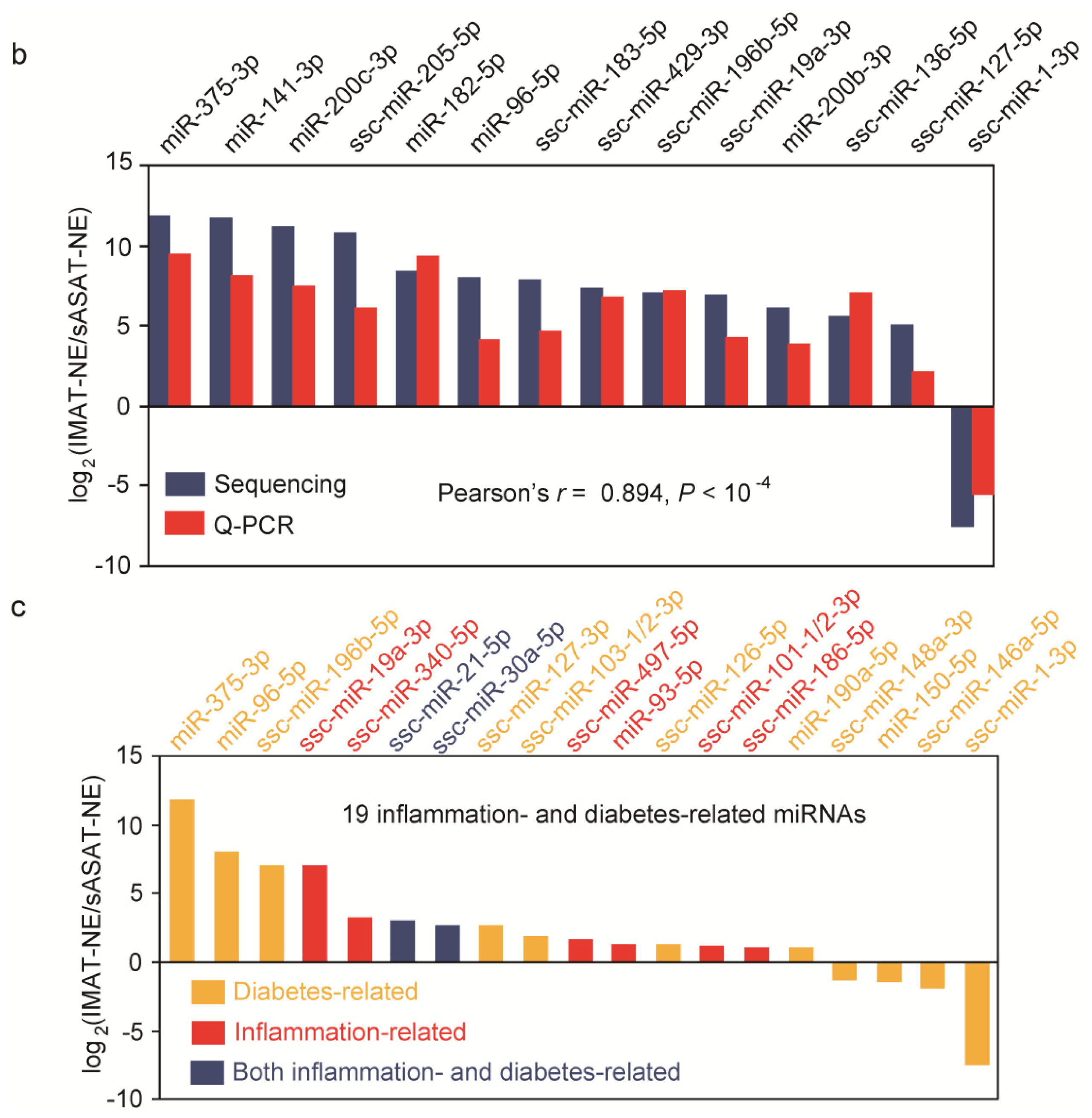
Characteristics of the differentially expressed (DE) miRNAs between porcine sASAT and IMAT
(b) q-PCR validation for the top 14 DE miRNAs with highest read counts between IMAT and sASAT. Pearson’s correlation was used to determine the relationship between the q-PCR and small RNA-seq results for miRNA expression levels. IMAT-NE and sASAT-NE represent normalized expression levels for the miRNAs in the IMAT and sASAT libraries, respectively; (c) The differential expression of 19 inflammation- and diabetes-related miRNAs between IMAT and sASAT.
Related Service
miRNA Sequencing Services – High-throughput sequencing is now available in addition to existing microarray and qRT-PCR profiling services for the most complete picture of miRNA expression in your samples. miRNA sequencing is a new method and a powerful tool to identify and quantitatively decode the entire population of miRNAs in your sample. [Learn more…]
Reference
Ma J, Yu S, Wang F, Bai L, Xiao J, Jiang Y, Chen L, Wang J, Jiang A, Li M. (2013) MicroRNA Transcriptomes Relate Intermuscular Adipose Tissue to Metabolic Risk. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14(4), 8611-8624. [article]