microRNAs (miRNAs) play vital roles in plants regulating a panoply of biological processes, such as development, hormone signaling, and stress response, by inhibiting target genes at the post-transcriptional level. However, the roles of miRNAs in Betula luminifera remain elusive.
To mine for B. luminifera miRNAs and targets, researchers from Zhejiang Agriculture and Forestry University recently utilized miRNA sequencing and degradome sequencing of mixed samples, including roots, stems, and leaves. A total of 114 known miRNAs or miRNA*s from 44 families, and 24 novel miRNAs and 17 miRNA*s plus 15 plausible miRNA candidates were identified, of which 36 known miRNAs, 29 miRNA*s, and all novel miRNAs had precursor sequences. Additionally, 49 targets for 19 known miRNA families and seven miRNA*s, and seven targets for novel miRNAs were identified using a high-throughput degradome-sequencing approach. The conserved miRNA targets were mainly transcription factors, whereas the miRNA* targets were mainly protein-coding genes, with preferential propensity to functional enzymes.
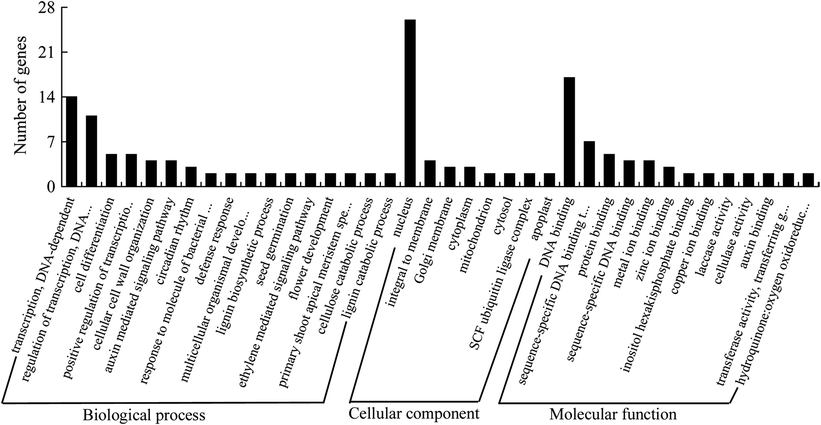
Histogram of the gene ontology classification
The results are summarized into three main categories: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC), and molecular function (MF). The Y-axis indicates the number of a specific category of genes within the main category
A Gene Ontology analysis showed that the predicted targets were classified into 62 biological processes, 20 cellular components, and 28 molecular functions, respectively. Researchers found two different targets for miR396a* and miR396c*, and the target changed when the miR156d precursor cleavage site was shifted toward the 5′-end by two nucleotides, indicating the diverse regulatory roles of MIRNA genes. Furthermore, three targets identified by degradome sequencing were validated further through 5′ rapid amplification of cDNA ends. The expression patterns of the randomly selected miRNAs varied among different tissues. miR164 expression was induced under nitrogen starvation, with tissue-specific expression patterns, and was negatively correlated with the NAC1 target gene in roots and leaves, but not in stems.
This study of transcriptome-based analysis of miRNAs and the degradome provides useful information for exploring the functions of miRNAs and their target genes in B. luminifera.
Related Service
miRNA/Small RNA Sequencing Service – miRNA sequencing is a new method and powerful tool to identify and quantitatively decode the entire population of microRNAs in your sample. LC Sciences now provides a comprehensive microRNA sequencing service. [Learn more…]
Degradome Sequencing Service -Degradome sequencing is a modified 5′-rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) with high-throughput next-gen sequencing method. Degradome sequencing has been use to identify microRNA (miRNA) cleavage sites, because miRNAs can cause endonucleolytic cleavage of mRNA by extensive and often perfect complementarity to mRNAs. Degradome sequencing has revealed many known and novel plant miRNA (siRNA) targets.…[Learn more…]
References
J. Zhang, M. Huang, J. Liang (2016) Genome-wide mining for microRNAs and their targets in Betula luminifera using high-throughput sequencing and degradome analyses Tree Genetics and Genomes 12:99 doi: 10.1007/s11295-016-1047-2 [article]