Understanding the metabolic and gene expression changes that accompany the expression of Yellow Canopy Syndrome (YCS) in sugarcane is important and could greatly assist in developing management strategies as well as in the identification of potential causal factors. Researchers from Sugar Research Australia analysed leaves representing two stages of development (leaves 4 and 6) from YCS symptomatic and YCS asymptomatic plants, from two seasons, using gas chromatography linked to mass spectrometry. More than 200 metabolites were detected in the leaf samples, and 84 of these could be identified. The results revealed intrinsic differences (p = 0.05) between the metabolomes of the YCS symptomatic and asymptomatic plants. It was evident that significant metabolic changes occurred well before the development of leaf yellowing. The major metabolic changes were associated with sugar metabolism, the pentose phosphate cycle, and phenylpropanoid and α-ketoglutarate metabolism. The diurnal changes of sucrose concentrations (low in the morning and high at the end of the day) are absent in the YCS symptomatic plants even before symptom expression. Comparing the leaf transcriptomes, by total RNA-Seq, of the symptomatic and asymptomatic plants shows that a complex network of changes in gene expression underpins the observed changes in the metabolome.
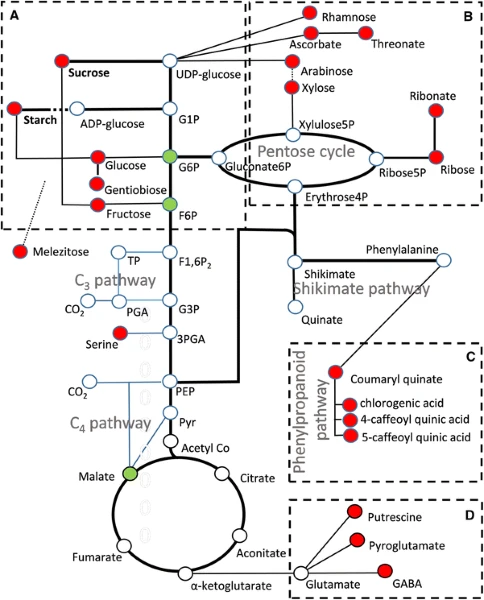
Mapping of the metabolites that change significantly (p ≤ 0.05) onto a simplified diagram of the metabolic network in the sugarcane leaf. Chemicals that were upregulated in the YCS symptomatic plants (red dots) and down regulated (green dots). Four clusters of metabolites can be distinguished (a–d). The open circles denote either chemicals that did not change significantly or included purely to complete the network diagram[/one_half][one_half]
Related Service
Total RNA Sequencing Service -Total RNA-Seq (Whole Transcriptome) sequencing captures a broader range of gene expression changes and enables the detection of novel transcripts in both coding and non-coding RNA species. Ribo-Zero ribosomal RNA reduction chemistry is used in place a poly-A tail selection which efficiently removes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) This process minimizes ribosomal contamination and optimizes the percentage of reads covering RNA species of interest…[Learn more…]
References
Marquardt A, Scalia G, Wathen-Dunn K, Botha FC. (2017) Yellow Canopy Syndrome (YCS) in Sugarcane is Associated with Altered Carbon Partitioning in the Leaf. Sugar Tech 19(6):647–655. [abstract]
